Physicist: The original post is here.
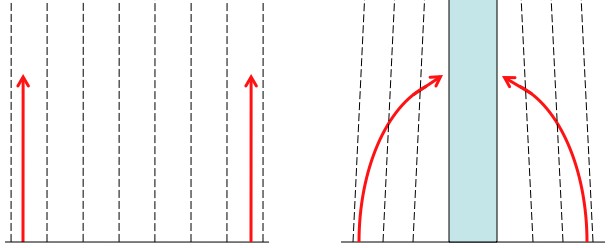
The curvature of space alone has almost no effect on the movement of objects until they are moving really fast. With the exception of only the most extreme cases (black holes), space is very, very close to flat. For example, the total stretching of space due to the Earth amounts to less than 1cm. The precession of Mercury’s orbit is another example of the tiny effect of the curvature of space (and it is tiny). Literally, there’s a little more space near the Sun than there “should” be, and as a result the direction in which Mercury’s orbit is elliptical moves. It takes a little over 3 million years for it to go full circle.
In almost all cases the vast majority of an object’s movement is tied up in its forward movement through time. The curvature of spacetime (not just space) is responsible for gravity. Literally, near heavy objects, the “future direction” points slightly down. So anything that moves forward in time will find its trajectory pointing down slightly. This takes the form of downward acceleration. This acceleration (time pointing slightly down) is entirely responsible for the motion of the planets, and every other everyday experience of gravity.
In flat space traveling forward in time has no effect on your movement through space. In curved space (e.g., near a large blue mass) parallel lines can come together, and moving through time leads to movement downward.
It may seem a little confusing that, once you’re moving, the explanation doesn’t change and falling is still caused by movement through time. Well, there is some effect caused by spacial movement and the spacial part of the curvature, but these effects are almost completely overwhelmed by the effects from the time component of the velocity (much, much bigger).

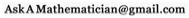




Assuming that a free falling object on earth is not pulled by gravity but is seeking a future time direction how does that object know that is the future direction?
This is for joe Tomas:
Joe did you get my response about Meryl: this is not for R. Crawford
Hi Gerard,
My apologies for delayed reply. I was not able to study Meyl after that !!
But question remains why pharma cos dont want to pursue things that may work.
Am on a tour so couldnt catch up. Shall email you as soon as im back to base.
Joe
Apologies but if curved spacetime is The new space plus absolute time – and geodesic trajectories are the new straight line, this “tiny” curvature as you put it fails to explain macroscopic effects like why a ball thrown in the air comes down in as little a space as my bedroom… Space must be very very curved down here and time moving very slow for such a macro phoenomenon !
About this concept of less space around massive objects, it has been linked to π. As you would probably know, the circumference is just slightly more than 2 times longer when compared to the length of its diameter. For simplicity, let’s say, exactly 2 times longer than its diameter. If the diameter is 1 unit, the circumference would be 3 units.
The question is: does this relation hold true for a perfect circle around the sun ?
Please, provide a complete analysis mathematical or descriptive.
Wouldn’t it matter how far away from the sun as compared to a circle in flat (special relativit) space?
all that exsists is a singularity
Most here forget Einsteins Equivalence Principle etc …
The Earth is accelerating at near or close to 68,000 m.p.h equivalent to 30 km /s or 18.5 miles per second ! around the Sun ….
The Earth is spinning at 1,600 kmh or 1,000 mph .. on its axis … 465 meters per second or 1,525 feet per second ….
When you toss an object up into the air its already traveling at 68,500 mph …. it has the kinetic energy of the earths acceleration eventually the Earth catches up to the object … The Earth and The Moon is in Free Fall around the Sun ” The whole Solar system is in free fall around the Galaxy … ! at 514,000,000 Miles per hour So you see Gravity equals acceleration + Curved space time ….
Don’t quite think that’s right as I understand it curved SPACETIME exerts a pressure on free falling object I.e. an apple and that kind of pushes it to earth while you’re on the earth stationary you are accelerating though time and you feel a push from the Earth on your feet or backside that you interpret as gravity. The General theory of relativity is highly mathematical I do not fully understand this took Einstein 10 years to figure it out the main maths is differential geometry and tensor calculus this he took 1 year to learn from his old classmate Marcel Grossman circa 1911-2 now a professor of descriptive geometry at his old uni.
I am trying to write a reply to G Crawford . I am not a Physics scientists and I am angry that. “ASK A MATHEMATICIANS” who keep sending me e-mail and NO BODY ANSWERS QUESTIONS FROM REPLYS. I’ll try one more time.
From what I can gather G Crawford thinks that Gravity is a force placed on falling objects but claims not to understand Einstiens General theory because it took him 10 years to develop. The fact that newtons F=MA. and GMM/R2 can predict weight and gravity well enough to land on the moon makes me wonder about the LINEAR ALGEBRA or whatever Einstein was using to predict why things fall. Are you falling when you get on a weight scale. NOW THAT II EXPRESSED MY CONSERNS I WOULD LIKE TO OFFER A NEW WAY TO LOOK AT THE DOUBLE HOLE EXPERIMENT AND THE SPEED OF LIGHT LIMITATION.
If you consider that electron wave interference only occurs when you do not use light to look at the double hole experiment.then I say that adding the light energy changes THE SPACE TEXTURE Close to the electron beam causing the beam to stop bring a wave and become a particle beam. The electron are always there but in some space texture they are waves and in another they are particles. Which brings me the final suggestion tha speed of light is space texture specific so that instantaneous(faster tha night) changes of quantum entanglement are representation of information transfer using another space texture,
Don’t worry Mr Crawford you don’t have to respond
Gerry Scally. jeliza3@gmail.com
There are two competeing Theories* 1 Newtonian Gravity 2 General Relativity ..
Newtonian Gravity although very precise boils down to an approximation …
General Relativity is more accurate for the past 100 yrs and not so long ago gravitational waves for the first time has been detected by LIGO ….
I’m a Ockum’S razor king of guy. Relative speed although I clearly exit has no impact on local gravity—- Newton is good enough
special relativity is calling that E= m c^2 e=energy , c=speed of light to follow this equation we can conclude that the force = momentum which diverts the meaning of both , another thing is that suppose we project two balls with the same velocity and have equal masses, at the same time, from the same point in the same frame of reference then the two balls should follow the same space -time curvature in their front movement and will come back following the same geodesic lines on their free fall then they should hit the ground at the same point and at the same time as if they are one mass , now let us consider one mass representing the addition of the two masses and do the same experiment by projecting the two original masses and project the some of the two masses then definitely they will not hit the ground at the same time and at the same point because they will not follow the same space time curvature and the same geodesic lines , i am afraid to say that the explanation of relativity theory to free fall may not seem to be as solid as in newton explanation that the force of gravity attraction is the reason behind free fall , and more over what happened to the acceleration of gravity which is 9.81 m/second square ,where is this constant in relativity ?, also time and space do not have the same units so to identify one point it has to be the point at the intersection of projections of all dimensions (x,y,z) all of the same units but how we can we project time to identify that very point if we are using space time system , please if you have clear understanding of the above mentioned points kindly advise – thanks for your anticipated cooperation
Can the above be used as a justification to why time slows down the deeper we go in a gravitational field?
thanks for your message , if i get it correct space curvature has no effect on object movement unless it is moving very fast , suppose we have object on free fall with normal speed then if it is not the gravity and we already excluded space time curvature as above then what is it that makes that object to fall ? either we should admit that it is solely gravity or it is the object is following geodesic lines attributed to space time curvature , please kindly give us a specific verification assuming that objects are moving with only normal speeds
Curved space seems like baloney. Does curved space effect a magnetic field?
I have never seen this explanation of gravity before, that it is almost entirely due to the curvature of time, as opposed to space. Could the author, or any kind commenter, direct me to other references which discuss this at length? ( Thanks)
then what causes free fall if not the gravity and not the time space curvature?
Wait, Why is time causing gravity? To my understanding i thought gravity affected time. Could you please explain.
Usually when someone can’t explain a complex topic in simple terms is because they don’t really understand it.
I know that they try to say gravity is just a curvature of space/time but it also may be due to gravitrons. We have not found them but that does not mean they don’t exist.
I prefer to think of gravity as a attractive force which pulls us down to the earth and it also can pull tug on the fabric of space/time. I don’t think of space time creating gravity its the other way round. More massive objects have more Gravitrons which attract things like a magnet even spacetime. Its weak so it takes something the size of the sun to bend it enough to see its effects. ie. Seeing a star that is behind the sun because the gravity of the sun curves the space time line.
Much like a bowling ball on a sheet of rubber bends the rubber so you could roll a small marble at the bowling ball on the sheet and it might curve right around the edge of the ball.
Just seems easier to think of gravity this way until someone figures it out.
Einstein NEVER said, nor promoted the wrong view that GR says gravity is the curvature of spacetime. Einstein viewed gravity very much as a FORCE. CORRECT YOUR ARTICLE.
Perhaps gravity can be defined as matter moving from where time is quickest to where time is slowest or stops completely. Each particle of matter causes time to slow, the greater the mass the slower the relative time occurs. Black holes would evidence where time stops.
Dr. Colebrook,
I’ve also found the idea that “…gravity can be defined as matter moving from where time is quickest to where time is slowest…” to be compelling. Time moves faster at my head than at my feet (while I’m standing, at least). Given that, and using conservation of energy (or the fact that travel through space-time is always c), it seems you would have to arrive at particles accelerating towards the center of mass. Is that reasonable?
John Nolan
curved space is gravitation no graviton particle is needed to transfer force matter is in fact traveling in the straitest line possible.
I would agree, particles appear to accelerate towards the centre of mass, the greater the mass the more time slows. The interesting question for me is how that process started. From the ‘big bang’ where time and space came into existence, matter/energy is moving from where time exists to where time stops, there must be some interaction at the quantum level to cause anomalies in space-time that slows time to attract matter. Otherwise everything, all matter and energy, would fly apart. Although galaxies are accelerating away from each other, at each centre is a black-hole where time is slowest or has stopped completely.
For a better explanation of what causes gravity just look at the equation for escape velocity Ve^2 = 2GM/r. That Ve^2 looks a lot like a field diluted C^2 and the C^2 looks a lot like the rest energy per unit mass of M. So why not spread the rest mass energy out as a field and call it gravity.
These are excellent original post and follow-up questions and discussions on the subject of space-time and gravity. Following are some of my thoughts on the matter. According to current theory, small pieces of randomly moving matter in space attract each other with their individuals minuscule gravitational fields and thereby eventually form increasing larger amounts of matter, eventually leading to the formation of stars and planets. The high concentrations of matter warp nearby space-time and create a gravity effect.
The Einstein field equations EFE describe the fundamental interaction of gravitation as a result of spacetime being curved by matter and energy. A re-interpretation of the EFE could lead to the following alternative explanation of how matter collects to form planets and stars, and how spacetime is warped by matter. Rather than matter first collecting, and then distorting space-time and thereby creating gravity effect, I hypothesize that discontinuous areas of SpaceTime could result in concentrated areas of gravity which then attract collections of matter. In a way, this is a reversal of the classic chicken (matter) or the egg (gravity) argument.
Lol nice troll question and you sucked in many. All these people wanting to answer “look at me I know” Well none of them know squat about it and only pretend to know.
Truth is we don’t know the “why” any other answer is just ego at work. And it may be the other way round opposite of the proposed question.
Next question…
I ask this question as a non-physicist
In their book The Grand Design, Hawking and Mlodinow insist that gravity existed prior to the existence of the material universe; indeed, they insist that gravity created it. It is my understanding that gravity is a product of locally warped spacetime, and spacetime warps because of matter, so it seems that the concept of gravity is quite meaningless without the existence of spacetime and mass. Can anyone enlighten me as to what Hawking and Mlodinow mean by this?
Tony
Tony – anyone who asks a question that produces months of silence is on the right track.
You have created a space of such (insatiable) gravitationally intense curiosity that it causes an internal gravitational explosion of anti-curiosity.
Eventually, due to the laws of psychic (not physical) gravity, a new supernova of curiosity will eventually be born.
But, in the meantime, time Slows.
This is the link between physical and psychic realities.
We only need weight ..
Hi Neil:
I wasn’t asking this question. I was wondering about Stephen Hawking’s point in his book The Grand Design that gravity (or the laws of gravity) created the universe. I’m not a physicist, but my layman’s understanding of gravity is that it is a warp in the fragment of spacetime caused by matter. Thus, I was confused as to how gravity can exist without there first (or simultaneously) being spacetime and matter.
Thank you for your response.
Cheers,
Tony
Yes, Tony – I was taking the further leap into the wild blue yonder – which does seem to be what the universe is mainly composed of ..
But my response to your more particular question would be:
Is mass the Only possible cause of gravity waves ?
Hawking implies that they existed either prior to, or as part of, BB.
But, if E really does = speeding Mass, then the BB itself could be these gravity waves exploding into near infinite mass.
All this shows how little we still know about just how energy and mass are related – and just how they may inter-transition and transform.
I suspect that full knowledge would literally blow our tiny minds.
But that brings us back to that apple from the tree of knowledge that eventually landed on Newton and now rests on the back of each iPhone ..
That’s why I think the physical and psychological worlds are not completely disparate.
Even the word “gravity” has feet in both worlds.
Thanks, Tony – Neil
Thanks, Neil.
Tony
This is a correct explanation of General Relativity. Now for the underlying philosophy: why does time move forward?
From all the comments i read, i conclude that none know even in slopped time geometry why objects fall? Assuming time-curvature adds more gravity-effect than space-curvature, objects can very well move from slower-time to faster-time.(away from heavy mass). Who concluded (math?) that objects have to move towards the future. Does current math reveal this? I have read the arrow of time has only one direction in the universe. Is it supported by math or math says it can be both directions?
In other words, does faster-time area (far from mass) have more potential energy than slower-time-area(near the mass), what gives the initial kick for object movement far away from the mass? The initial bigbang? Since nothing is stationary in the universe, Unless the object is out of the current Bing Bang universe, I assume/guess even in far away area from gravity-mass there is an infestimal small time curvature due to existance of closed universe for oject to start initially moving nad later encountering gravity masses.
If the earth catches up with an apple falling from a tree, why doesn’t a falling apple on the opposite side of the earth fly up into the air and end up in space?
@Jerry Sawyer
You’ll sometimes hear gravity described as space itself flowing downward and carrying material with it, like a leaf being carried toward a drain. This isn’t a great metaphor, but it gives you a sense. The surface of the Earth accelerates upward everywhere. I really wish there were a better way to say that without sounding crazy.
Well thank you so very much for that info. I didn’t want to sound completely ignorant. 😊
Actually, I do have one more question. Could you tell me a little about how the curving of space time caused by the moon causes the ocean tides in Earth. This one drives me crazy.😊
@Jerry Sawyer
Looking at the tides in terms of curved spacetime is bringing an aircraft carrier to a knife fight: way more work than you need to do.
The Moon and Earth orbit each other (because they both have mass), but the center of their orbits is a few hundred miles below the Earth’s surface (because the Earth has a lot more mass). The side of the Earth closer to the Moon is pulled on more, so the water rises a little higher there (a dozen feet is very little compared to the size of the Earth). As the Earth “wobbles” around the center of its “orbit”, the side facing away from the Moon swings more and the water on that side sloshes outward and thus higher. There’s your two tides: one when the Moon is overhead and the other 12 hours later.
I believe the original question was calling Hawking’s notion that the laws of gravity created the universe, and that can gravity be said to exist absent mass, into question. Can we talk of gravity at all absent mass?
Thanks again. I do understand your description of how gravity causes the tides on Earth. What I don’t understand is how the warping of space time actually causes what we observe as “gravity”. I have studied some math and physics, and it seems I should be able to understand this.😊
Why does “curved space-time” cause gravity?: A better answer.
In general relativity, gravity is not a force but a geometric phenomenon.
Rather than thinking of gravity as a force like a magnet acting on a steel ball. Think of it as bending of space/time. The analogy of a a bowling ball on a thin rubber sheet works for this. Place a marble on that bent sheet and it will roll towards the bowling ball.
We are falling towards the center of the earth all the time. But the earth gets in the way, preventing us from falling to the center. Some say its pushing up at us. Not really its just getting in the way. If you were on a ship accelerating at 9.8 m/s squared you would feel the same thing. The ship is not creating gravity but the sensation is the same. Its a pseudo force.
The earth stops us from falling, this opposing force is termed normal force. This is what you “feel” while standing on the earth. If we could make the earth vanish (but keep the bent spacetime or gravity in place” you would fall towards the center of the at 9.8 m/s squared. Since the normal force is gone (we made earth disappear) you would feel weightless.
So mass tells space how to bend. And objects in this space fall from areas of low to high gravity. or from areas of less bent spacetime geometry to more bent. Or in the case of the bowling ball analogy from areas less curved to more curved.
But how does mass perform this trick on space-time? Maybe a gravitron is interacting with spacetime and not directly on us? Not found a gravitron yet. But even if we do the same rules will apply.
Thank you so much Bob. This is very helpful. Now all we need to do is find that graviton.😊
Oh that would be big news finding a graviton! We live inside a big puzzle the answers are hiding in plain sight.
I think someday we will find a way to counter act gravity.
In 1968, I studied nuclear sciences. At the time, we were told about a new sub atomic particle had been discovered and named a quark. And that protons and neutrons contained three quarks. They told us there were several types of quarks, but very little has been written in college textbooks about it. So we were told, we will not be studying the subject.😊
Scientists have learned a lot.😊
What the universities are working on and what the subcontractors and military can be two different things. Too secretive for me and waste of time working on something tha has already been done by another party. Also way too slow waiting for cyclotron time (1 year) for simple experiment that usually yields very little.
I love this discussion as I spend most of my time thinking about it when my mind is not otherwise occupied. Sometimes I think about it when I should be thinking about something else which gets me into trouble. 😉
I think gravity is the result of mass taking up space where space-time should be. Imagine space-time as a piece of foam that fits perfectly in a box. If you place a golf ball on top of the foam and close the lid, the ball makes an impression on the foam because it has no way of being displaced like water would. Because space and time are hard to move, this resistance causes a force back onto the mass directly related to the amount of mass. This is gravity. “Space-time’s resistance to bend to mass causing an equal and opposite reaction around the mass.” The larger the mass, the larger the force.
(I am simplifying of course. Because space-time does not act the same way as foam against a ball which would only squeeze the ball due to the tighter fabrics of foam around the ball, but somehow space-time resists mass in such a way that it causes the mass to attract everything near it.)
If we want to understand the force of gravity better, we need to consider the effect of time manipulation. If we could stop time around the earth, I think gravity would disappear. Would we then go floating away? No, because that would take time.
Black holes show us that if the mass is large enough, not only does the force of gravity (time-bend resistance) get so strong that light cannot escape, but time can slow down (bend) significantly.
I also think that the speed of light has nothing to do with the rate at which light particles can travel, but the willingness of space-time to allow it to go without bending too much. Go faster than the speed of light and space-time must change to accommodate. (i.e Time bends)
This leads me to time travel. I don’t think it is possible, but theoretically we should be able to witness any point in time, by looking at earth with our backs to a black hole and getting close enough see the entire history of the universe as we move closer.
Thoughts? (other than, “this guy is wacko”)
A good understanding of the relationship of space to time i.e. ‘space-time’ can be found here: https://youtu.be/au0QJYISe4c
nice article
But exactly what gravity is or how it propagates