Physicist: In a word: no.
A reactionless drive is basically a closed box with the ability to just start moving, on its own, without touching or exuding anything. The classic sci-fi tropes of silent flying cars or hovering UFOs are examples of reactionless drives.
The problem at the heart of all reactionless drives is that they come into conflict with Newton’s famous law “for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction” (hence the name). To walk in one direction, you push against the ground in the opposite direction. To paddle your canoe forward, you push water backward. The stuff you push backward so you can move forward is called the “reaction mass”.
This is a universal law, so unfortunately it applies in space. If you want to move in space (where there’s nothing else around) you need to bring your reaction mass with you. This is why we use rockets instead of propellers or paddles in space; a rocket is a mass-throwing machine.
But mass is at a premium in space. It presently costs in the neighborhood of $2000/kg to send stuff to low Earth orbit (a huge improvement over just a few years ago). So, the lighter your rocket, the better. Typically, a huge fraction of a rocket’s mass is fuel/reaction mass, so the best way to make spaceflight cheaper and more feasible is to cut down on the amount of reaction mass. The only way to do that at present is to use that mass more efficiently. If you can throw mass twice as fast, you’ll push your rocket twice as hard. Traditionally, that’s done by burning fuel hotter and under higher pressure so it comes shooting out faster.
In modern rockets the exhaust is moving on the order of 2-3 km per second. However, your reaction mass doesn’t need to be fuel, it can be anything. Ion drives fire ionized gas out of their business end at up to 50 km per second, meaning they can afford to carry far less reaction mass. Space craft with ion drives are doubly advantaged: not only are they throwing their reaction mass much faster, but since they carry less of it, they can be smaller and easier to push.
The drawback is that ion drives dole out that reaction mass a tiny bit at a time. The most powerful ion drives produce about 0.9 ounces of force. A typical budgie (a small, excitable bird) weighs about 1.2 ounces and, since they can lift themselves, budgies can generate more force than any ion drive presently in production.

Compared to rockets, ion drives pack a greater punch for a given amount of reaction mass. However, they deliver that punch over a very long time and with less force than a budgie.
Given the limitations and inefficiencies, wouldn’t it be nice to have a new kind of drive that didn’t involve reaction mass at all? You’d never have to worry about running out of reaction mass; all you’d need is a power supply, and you could fly around for as long as you want.
That’s not to say that propellantless propulsion isn’t possible. There are ways to move without carrying reaction mass with you. You can use light as your exhaust (a “photon drive”), but you’ll notice that a flashlight or laser pointer doesn’t have much of a kick. And you can slingshot around planets, but then the planet is your reaction mass.
The problem with reactionless drives, fundamentally, is that Newton’s third law has no (known) exceptions. It is one of the most bedrock, absolute rules in any science and a keystone in our understanding of the universe. On those rare occasions when someone thought they had found an exception, it always turned out to be an issue with failing to take something into account. For example, when a neutron decays into a proton and electron, the new pair of particles don’t fly apart in exactly opposite directions. Instead, the pair have a net momentum that the original neutron did not.
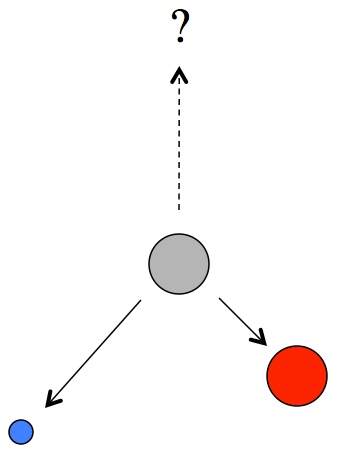
When a stationary neutron (gray) decays into a proton (red) and electron (blue), the new pair flies apart, but always favor one direction. Newton’s laws imply that there must be a third particle moving in the other direction to balance the other two.
The implication (according to Newton’s law) is that there must be another particle to balance things out. And that’s exactly the case. Although the “extra particle that’s really hard to detect” theory was first proposed in 1930, it wasn’t until 1956 that neutrinos were finally detected and verified to exist. The imbalanced momentum, a violation of Newton’s laws, came down to a missing particle. Today neutrinos are one of the four ways we can learn about space, along with light, gravity waves, and go-there-yourself.
There are plenty of ideas floating around about how to create reactionless drives, such as the Woodward Effect or the Albecurrie warp drive. But in no case do these ideas use established science. The Woodward effect depends on Mach’s principle (that somehow inertia is caused by all the other matter in the universe), and reads like a pamphlet a stranger on the street might give you, while the Albecurrie drive needs lots of negative energy, which flat-out isn’t a thing.
Science is all about learning things we don’t know and trying to prove our own theories wrong. While scientific discovery is certainly awe inspiring, it is also the exact opposite of wishful thinking. That said, good science means keeping an open mind much longer than any reasonable person would be willing to. In the ultimate battle between theoretical and experimental physics, the experimentalists always win. If someone ever manages to create a self-moving, reactionless drive, then all the theories about why that’s impossible go out the window. But as of now, those theories (standard physics) are holding firm. We can expect that for the rest of forever, all space craft will have a tail of exhaust behind them.






Kind Readers,
One of my personal heroes is Kelly Johnson. Born in an obscure town in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. As a student at the University of Michigan, he performed wind tunnel testing on the P-38 Lightning and contributed to the design. Importantly, he was the founder of the Skunk Works at Lockheed . A selection of his accomplishments include leading the team for: first US Jet, the U-2 Spy plane (he advised the government to fly if for only two years, but they flew it for four), the record holding SR-71, etc. His successor was a fellow by the name of Ben Rich, who wrote a book worth reading about the Skunk Works. On his death bed, Mr. Rich reportedly stated ‘Anything you can imagine, we can do’. I can imagine quite a lot, but have seen a few things outside the bounds of commonly known physics… which is ‘division’ of math.
In my college years (circa early ’90s) I saw a news brief showing a video recording from an Astronaut aboard the Space Shuttle. It showed a bright object approaching the Earth, and suddenly two very fast objects from Earth’s surface were ‘sent?’ at it (Earth to orbit in about a second, not laser beams), and the approaching object made a V turn, yes V turn, and moved out of camera. I looked for the video on YouTube since then, but the video was highly degraded. I am a trained theoretical and empirical scientist and know what I saw; I wouldn’t bother typing this if it weren’t factual. The ‘official’ explanation was that it was space dust bouncing off the window. This is highly, highly improbable.
I’ve taught my kids F=MA and about the equation’s discoverer. If M drops to zero, somehow, then F and A could be whatever you want them to be. All I am saying is all. I’ll race you all to figure it out and put the folks at JPL to shame… or prove me wrong.
To paraphrase Shakespeare: There are more things in Heaven and on Earth that can be dreamt of by our philosophers, and you my friends are great philosophers if you know it or not.
Isn’t the warp drive concept also sort of reaction propulsion which reacts with space itself ? Like the canoe example the drive pulls space infront of it and than pushes it around and behind it (similar to diver in deep sea that swims).
And also why is it imminently considered that the Alcubierre drive always needs negative energy densities ? For example, according to my humble understanding of cosmology and relativity negative pressure should also do the bending space-time trick. And there are actually known phenomenons which rely on the effects of negative pressure: the cosmological constant/vacuum energy (if we could manipulate it) and the inflaton field that drove the universe’s expansion (if we could reproduce it somehow).
Since space is an almost perfect vacuum, would it be possible to make the space in front of you less dense than the space behind you causing you to move forward? Obviously that wouldn’t be easy, would it work?
When hot gases leave rocker nozzle, the particles move chaotically and not only in the direction opposite to the rocket flight. So great part of energy is wasted. Is there a way to make all particles (say atoms) to move just in one direction? Kind of laser but not of photons but of atoms, so all of them are coherent and move in exactly same direction?
@Leo
“Coherent matter waves” (mass lasers) are a thing, but they’re far more trouble than they’re worth in this case. Even coherent beams have some spread; there’s no way to get it to zero.
If you look at the exhaust from a rocket it does form a cone, but it’s a pretty sharp cone. It’s mostly going in the right direction.
@Edwin Friskey
There are a couple of ideas that are close to that.
A “ramscoop” is a hypothetical (but fairly reasonable) device that would use big magnetic fields to direct the stray ions in front of a ship into a scoop to be used as fuel.
A “solar sail” is literally just a really big, really light-weight sail that catches light (photon pressure) and solar wind flying out of a star. Solar sails are an extremely efficient way to move around in a solar system, if you’re not in any kind of hurry.
@Pavel Aymaliev
Unfortunately, space isn’t a substance that can be grabbed. If it could be, then we’d have a way to determine whether or not something is moving (by dropping a “space anchor”), which is a big violation of the base principles of relativity.
Dark Energy, assuming it is an actual “stuff” that exists rather than a mathematical artifact, seems to have an absolutely fixed density. Alcubierre’s warp drive requires us to be able to manipulate how that energy is distributed. But as of now, we don’t know how to do that, whether it’s possible, or if the stuff we want to manipulate even exists.
That could certainly change in the future, but I wouldn’t hold out too much hope.
The question is, can you push against the quantum vacuum? That’s the question being asked by the NASA team who test new ideas for drives, some of which seem to work at this stage, according to papers they’re published, though it’s too early to tell.
We know there’s energy in the vacuum, it was predicted by quantum field theory, and then confirmed by experiment, with the Casimir effect. Experiment gave the same number as theory. But when we try to calculate the vacuum energy another way, we get a number 120 orders of magnitude different. This enormous discrepancy, the vacuum catastrophe, means that if you ask, do we know enough about the vacuum energy to answer the question about whether a drive could push against it, the answer would unavoidably be ‘no way’.
@ The Physicist: yes, the gas jet from the nozzle has nearly straight shape, but the atoms in the jet move chaotically, i.e. in all directions, because the gas is very hot. If it were nearly absolute zero temperature and moving just in one direction, then energy would not be wasted, right?
@Leo
Being hot means there is variation in the velocities of the exhaust molecules. But ultimately, they’re going in the right direction, so that variation takes the form of some of them traveling a little faster or slower than the mean. If you look at a rocket when it’s active, there isn’t a lot of gas spraying out sideways. Heat does make it spread out faster, but it’s not a major hurdle.
Just one small point. If you have a limited supply of ejection mass available for propulsion then you must eject it at as as high a velocity as possible…but that raises a question. In the text, a statement to the effect, says if you eject at twice the speed you get twice the reaction…of course…but if you are talking kinetic energy then doubling the speed of ejected mass quadruples the kinetic energy…i.e. E=1/2 mv²….so there.
Seems the ultimate solution is to minimise the exhaust while maximising the applied energy. Couldn’t a COIL in a solenoid in a rocket be “moulded” by the thinnest of conductive plasma or gas – and then be supercharged by an onboard generator/capacitor. Thus the coil becomes the propellant
I am out-thunk by Craig in that I have no idea what he is talking about….
I get that a lot. I remember Einstein’s statement that only half a dozen people really understood relativity.
I thought for a moment you could be right … but then thunk that was inthunkable.
The trouble with not understanding other people’s thinking is that you are never sure where the deficiency lies…a sublimating solenoid moulded from thinnest of plasma leaves me defenceless. I just CANNOT envisage such a thing…and I have been making plasma, winding solenoids and sublimating for 50 years. Help me. You might be on to something…or a complete numpty. I know the feeling.:)
I have seen a space ship up close and watched it propel into space from 50 ft above the earth, the propulsion method had no noise like a rocket or jet, it was gone out of sight in 3 to 4 seconds with no air blast behind. I never felt any wind and there was no burnt grass left behind. All propulsion methods we have make lots of noise and leave a blast in there wake and we also cannot stand close to one of our rockets taking off or we would be blown away or burned up. From seeing this close up, i know there is an alternative propulsion method that we have not discovered yet. *** I hope to find it !!!
In a word: YES, reactionless propulsion is possible – by properly using Lorentz force.
My email address is htg@interia.pl
I just want to say this. The only true closed system in the universe is the universe itself.
So its a logical fallacy to call a black box a closed system. What you actually mean it is a macroscopically closed system.
Energy in the form of electromagnetic fields interact with the interior, particles such as nuetrino’s constantly pass through it. Gravity (mass/time distortion) interact with every thing inside it.
A quote from a famous physicists dad sums it up…
“My father taught me to notice things. One day I was playing with an “express wagon,” a little wagon with a railing around it. It had a ball in it, and when I pulled the wagon I noticed something about the way the ball moved. I went to my father and said, “Say, Pop, I noticed something. When I pull the wagon, the ball rolls to the back of the wagon. And when I’m pulling it along and I suddenly stop, the ball rolls to the front of the wagon. Why is that?
“That, nobody knows,” he said. “The general principle is that things which are moving tend to keep on moving, and things which are standing still tend to stand still, unless you push them hard. This tendency is called ‘inertia,’ but nobody knows why it’s true.”
– Richard Feynman
So I hold out hope because its the only true way we will explore this solar system and beyond (in the near future).
I also have a theoretical model that definitely does not break the third law. Sadly my maths is not good and I need(want) to create a mathematical model before I move on to a physical test.
Chris…try the same experiment with a helium filled balloon in a car. As the car accelerates the ballon goes to the FRONT of the car…when you brake it goes to the back. Similarly, (and for the same reason) a candle flame on a record player periphery bends in to the centre…nothing mind-blowing…and off topic BUT all very counter-intuitive IF you don’t know why.:)
Actually.. Reactionless Drive has been demonstrated using Quantum Tunneling.
Chris … Tom’s experiment with the helium balloon is not quite the same thing. It’s movement has nothing to do with it’s inertia, it’s the inertia of the air that compresses at the front of the car when the brakes are applied, and the balloon is pushed toward the back of the car by buoyancy, where the air is briefly less dense.. Yes, there is some inertia of the balloon to move forward, when the car slows; however, buoyancy has the greater influence.
The candle thing is also not the same experiment. We assume the candle is moving in air (because it is burning) and the candle is moving in a circle, and therefore accelerating toward the center of the circle. We assume the candle is inside a jar, like the closed car. and thus the jar and the air inside are experiencing continuous acceleration toward the center of the rotation. This is not the same thing as a candle on a record. the flame in the jar will point toward the center of the circle of rotation, again because of the density change of the air inside the jar, which is spinning as if in a centrifuge. the heat (flame) moves toward the less dense air .. toward the center of the centrifuge. None of these experiments have anything to do with a reactionless drive … or, action without re-action.
Thanks Micheal. I think your response is spot on.
I would think that it would be far easier to create an electro-magnetic field gradient about a ship , than a gravitational one . A nuclear reactor could power the first one , but a thousand reactors would be inadequate for the second one . Also , we know how to manipulate EM fields , but flub at grav ones.
P.M.
Point 1. We need to stop over applying the third law. We know it is a law of mechanics, not physics. This distinction is not mere word play. We know ( see Griffith’s E&M or Goldstein Mechanics that 3rd law doesn’t apply when you have fields.
But, of course, momentum conservation still holds and a theorem from this tells us that the velocity of the center of mass of an isolated system moves at a constant velocity.
It is this theorem that says no reactionless drives.
Point 2: There is a distinction between existence of a reactionless drive and a useful method for moving through space. If a reactionless drive exists, it may not be useful. Is it still interesting?
Well, I`m also a physicist an I`ve performed exhaustive tests on prototypes over the last 10 years. Several possible systems I rejected as the experiemtns showed the theory to be in error. But 2 systems survived the white heat of trial by experiment – the Lorentz force and an inertial system. I`developing these now as the only way to break throguh the stagnation in propulsion physics is to give a good demo of a car moving with no contact to the wheel or a floater – a cube hovering and dating about in response to a remote control. All absolutely possible. Every law has exceptions – this is true on maths (Gödel`s theorem) and also in physics. Yes, lots of what will later be seen as crap in physics books will have to be re-written. Look out for developments in the next few years.
When two black holes of different mass merge, the merged object experiences a “kick” because net linear momentum is carried away by the gravity waves emanating from the event.
So I guess a hypothetical reactionless drive could emit gravity waves to push against spacetime. On the other hand, creating those waves probably takes so much energy that (by E=MC^2) the drive isn’t really reactionless .
@Wim Coenen
That’s why physicists are a little careful to use the word “reactionless” and not “massless”. You can use both light and gravity waves to propel and object, but we presently find that mass (literally throwing something in the opposite direction) is by far the best way of moving around in space. Photon drives (giant flashlights) and light sails are very real things, but gravity wave drives are a little outlandish. If you want gravity, you need mass. Generating gravity waves means swinging really large masses really fast, so a gravity drive would (as far as we know) basically come down to putting yourself in (high) orbit around a pair of black holes that are about to merge and fly off in the direction you want to go.
Imagine, a magnetized core containing Gadolinium. Wrapping the core with heavy duty wire through which a high voltage current is producing a strong magnetic and a weak gravitational field. The difficulty is aligning the field with a dark energy field and producing a directional force which can be controlled and used to move things in space.
If the dark energy and matter share gravity with a parallel universe, there should be a way to push and pull against it to create a massless drive
When I was studying engineering, in the early 1990’s. I was studiously watching the Simpsons, and a local news program came on during a break which showed amateur footage from the Space Shuttle. It showed, in vivid clarity, a shining object approaching the Earth; two darts of light went towards it (not fast enough to be lasers, not slow enough to be known). When the ‘darts’ got near the object (from Earth’s surface to space in about a second) the object made a V turn (known physics impossible) and went out of camera. The video has since been degraded/scrubbed. NASA replied it is just random particles on the window. I have a highly technical background and know what I saw. Methinks someone has figured out how to minimize or eliminate the M in F=MA.
Hi there,
Please have a look at the link below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xX14NK8GrDY&ab_channel=PeterAxe
As if a kind of a reactionless drive principle is already confirmed?
Looking forward to your answer.
Nothing in that video nor anything in the forums or hand written text actually show a reactionless drive.
There is no evidence for the statements you make. Had you set up and shown an actual experiment that some how confirmed the statements you made I am sure more people would be interested.
However some of your assumptions seemed based in fantasy and have no relevance to a reactionless drive.
Your statement on overunity.com that “you have to be an expert in the field of theoretical and applied mechanics” is complete rubbish, anyone with a little bit of experience will understand that transfer of forces from the plunger to the container walls. there is no breaking of any laws there.
My one suggestion is to rewrite everything you wrote to better explain what you are trying to describe. Your explanation is very unclear. Add an actual video of the complete experiment. If you don’t have the energy or resources to create the experiment for something you believe in why do you think anyone else would?
My one question for you is this. Where is the source of energy and how does it interact with your “device”?
To Chris.
———————————
You may have watched our video but you have not understood anything. Are you really such an ignoramus? Or may be as a payed agent of the official science mafia you simply imitate ignorance and pathological lack of understanding thus trying to manipulate the audience in a clumsy and unskillful manner? Shame on you!
———————————
1) I am asking you my first question. And the question is: Do you accept the simple fact that modern technologies allow reducing of friction practically to zero thus practically reducing to zero (to a negligible value) the experimental error due to friction? Yes or no? (Your answer must consist of one word only — either “yes” or “no”.)
———————————-
2) I am asking you my second question. And the question is: Do you accept the validity of the simple experimental fact (WATCH CAREFULLY OUR VIDEO!) that the zigzags generate mechanical resistance, (a) which is absolutely identical and equivalent to friction and (b) which does not generate heat? Yes or no? (Your answer must consist of one word only — either “yes” or “no”.)
I love your conversation guys, especially its temper, and I am impatiently waiting for the continuation.
Lol Leo.
You won’t get anything more from me, I know when I am completely outclassed and out intellected.
He totally decimated the people at scienceforums I believe they pay homage to him on a weekly basis now.
I’ve been intrigued by the fact that while linear motion is relative, rotational motion is absolute. I’ve toyed with the idea that energy can somehow transferred from a linear impulse to a rotational impulse at right angles to the direction of motion and dissipated as thermal energy. Classical physics says no. But…what about a superconducting torus? Imagine a stream of charged particles passing through the center of a superconducting torus. The energy charge of the particles is enough to briefly overcome the Meissner Effect resulting in an electromagnetic impulse being transferred to the torus at right angles to the flow direction of the particle stream. The energized electrons will flow around the torus at zero resistance thereby taking some of the momentum energy away from the particle stream. The edge of the superconducting torus is kept at a temperature above the critical point resulting in some of the electrons losing their energy as dissipated heat. The particle stream is diverted around the torus and accelerated with more energy to continue the process. In this way energy is conserved but perhaps momentum is not, resulting in forward motion. Just a thought. I don’t have the equipment to put such a device to a test but perhaps someone else can.
You are wrong, reactionless thrusting is now possible.
Just take a look t this short explaining video:
On October 28, 2024 I did a test on a device that produced what could be call reactionless propulsion In this test there was a weigh that could move inside a closed box the weight was move forward without effecting any Actions or counter reactions on the box’s movement once the weight hit the front end of the box the box moved forward The weight then returned to the back end of the box – producing no action or counter reaction to the box’s movement in any direction. after 20 cycles the box moved 1 and 1/2 inches from the starting point sitting on the table top flat ( no rollers were used ) The formula is ( 2 energy forces used for 1 output Action device )
The weight was about 6 grams and the box weighed about 2 lbs
( Is reactionless propulsion possible ? ) Well I know it is – If you want to see the drawing to the concept of the technology find Dr. Wlazlak and ask
Hello,
Equal and opposite forces are not a sufficient condition to prohibit reactionless motion. There are more than ten other conditions. Here are two of them:
1. When we say that equal and opposite forces prohibit reactionless motion, we are assuming, without realizing it, that both forces can only do one thing – accelerate according to the Second Law. But what will happen if one accelerates and the other overcomes inertial resistance?
See the preprint “Step Derivative equations of inertial motion in the Classical mechanics. Conservation Laws”
https://www.lifescience.net/preprints/most-discussed/?&preprints_by_type_filter=2&filter_action=del
2. Newton’s laws are reversible. The reversibility of the transformation of quantities and qualities is an absolute condition for the action of the Conservation Laws. But what will happen if there are irreversible inertial interactions?
See the preprint: “One way equations in the Classical Mechanics. Conservation Laws”